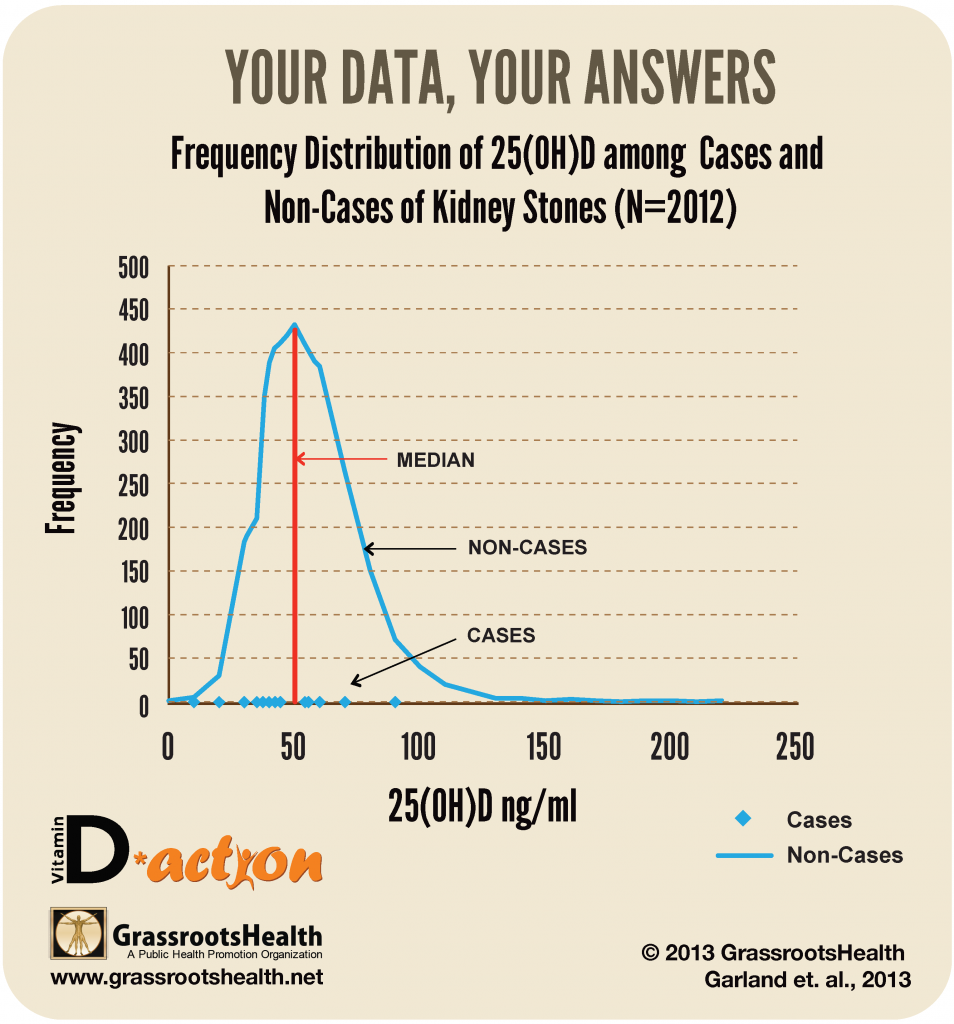
One of the misconceptions about vitamin D is that increased vitamin D levels can increase the risk for kidney stones. Upon examination of the D*action population, GrassrootsHealth was able to show an opposite effect.
Of 2012 D*action participants who had submitted at least two health questionnaires and vitamin D blood tests, 13 reported an occurrence of kidney stones after their first test. Of the 13 cases, eight were below the median serum level of 50 ng/ml (125 nmol/L) and five were above.
Those with vitamin D levels greater than 57 ng/ml (142 nmol/L) had a 60% lower risk of developing kidney stones compared to those with concentrations below 42 ng/ml (105 nmol/L). Also of note, individuals with a body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 30 had a 3-fold higher risk of developing kidney stones.
Source
25-Hydroxyvitamin D in the Range of 20 to 100 ng/mL and Incidence of Kidney Stones
Stacie Nguyen et al.
American Journal of Public Health
October 2013
